Yes, this is an expanded version:
Understanding Heart Attack: Early Signs, Precautions, Pain Identification, and Prevention
Early Signs of a Heart Attack
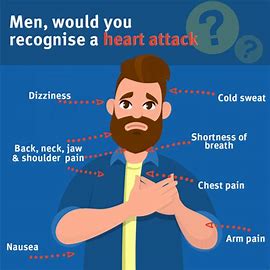
Early identification of a heart attack is important and can play a critical role in successful intervention and treatment. The symptoms, though varied, include but are not limited to:
- Chest Pain or Discomfort: This is the most well-renowned symptom. The pain is often described as pressure, squeezing, fullness, or discomfort in the center or left side of the chest. It may last for a few minutes or may be intermittent. The pain may be mistaken for heartburn or indigestion, but it is often more intense and persistent.
- Pain Radiating to Other Areas: Pain from a heart attack may radiate down the arms-for most, it’s the left arm-shoulders, neck, jaw, back, or stomach. This radiation can at times be mistaken for other conditions such as muscle strain or gastrointestinal issues.
- Shortness of Breath: This may occur with or without chest discomfort and is described as not being able to catch your breath or feeling as though you are breathing heavily without exertion.
- Associated Symptoms: These may include nausea, dizziness, or a cold sweat. In women and in some other individuals, the symptoms may not be so typical but can be extreme tiredness or a feeling of doom.
Precautions to Reduce Risk

One can considerably decrease the risk of having a heart attack by following certain precautions. The major ones include:
- Follow a Heart-Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins-soy, fish, and poultry-and healthy fats, such as nuts, seeds, and avocados. Limit saturated and trans fats, cholesterol, and sodium; excessive intake may lead to heart disease.
- Exercise Regularly: Do at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise throughout the week, or a combination of both. Also, include muscle-strengthening activity on at least two days of the week. Activities may include brisk walking, cycling, swimming, and jogging.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for heart disease. Quit smoking can improve heart health and reduce the risk of heart attack, thus enabling one to enjoy life with better quality.
- **Limit Alcohol Consumption: If you choose to drink, do so in moderation. This generally means up to one drink per day for women and up to two drinks per day for men.
- Effectively Manage Stress: Chronic stress is unhealthy for the heart. Engage in meditation or yoga, or any other activities that may lessen your stress, with the help of a professional therapist. This will enable you to effectively let out your stress and manage your life better.
- Monitor and Manage Health Conditions: Keep a chart on blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and levels of blood sugar. Follow the advice given by your health professional regarding the management of conditions such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Overweight or obesity can raise blood pressure. Reaching and maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can lower the risk for heart disease.
Identifying Heart Attack Pain
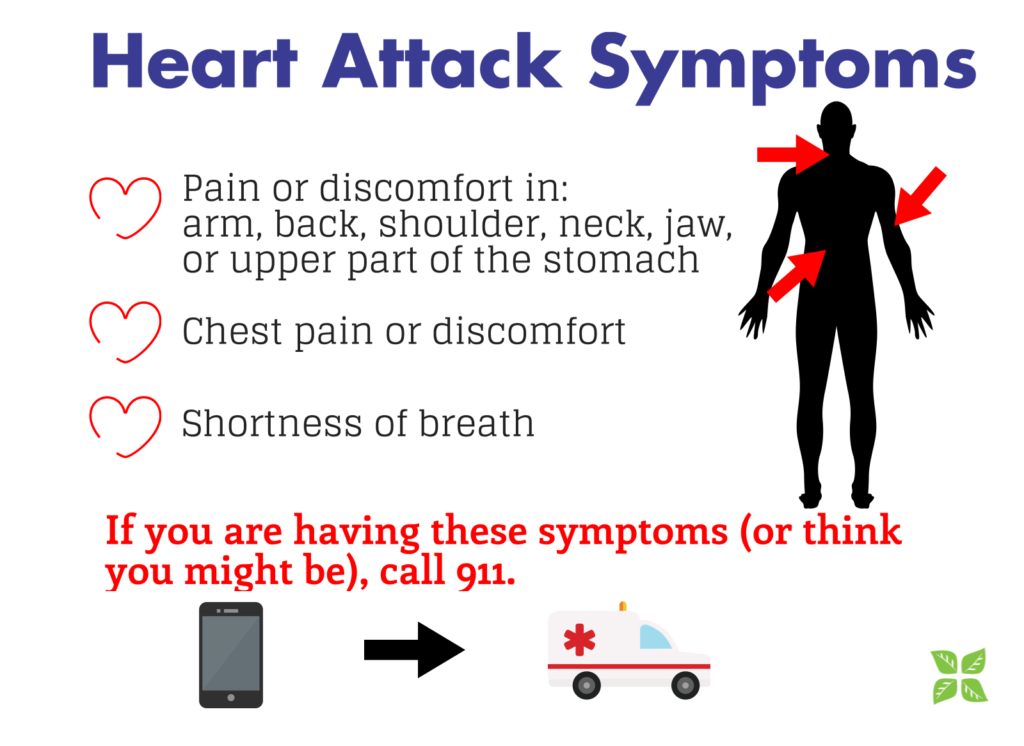
The nature of heart attack pain is such that one needs to understand it for quicker response. Some of the important characteristics include:
- Location of Pain: Pain from a heart attack generally centers in the chest or on the left side of the chest. The pain may also radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, back, or stomach.
- Type of Pain: Pain will often be described as pressure, squeezing, fullness, or aching rather than as sharp, stabbing.
- Duration: The pain may last or come and go repeatedly for a number of minutes. Chest pain that persists or recurs needs immediate medical attention.
- Associated Symptoms: Other symptoms such as shortness of breath, nausea, sweating, dizziness, or lightheadedness are crucial to effectively distinguish heart attack pain or discomfort from other causes.
Prevention Strategies
Effective prevention can go a long way in decreasing the chances of a heart attack. Here’s how:
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular check-ups with your health provider will keep tabs on the risk factors and help manage them in time. Regular check-ups will show you your problems before they become serious.
- Cholesterol and Blood Pressure Management: Maintain both cholesterol and blood pressure at recommended levels. Dietary corrections, exercises, and medication will keep these at normal levels.
- Adherence to Medications: When medication is prescribed for conditions such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, or diabetes, take the medication as instructed. Consistency in medication may enable the prevention of complications.
- Health Screenings: Regular screening for blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and blood sugar will help in identifying potential problems early and thus provide for early intervention.
- Educate Yourself: Stay updated with the essential information about heart health, including awareness about the most recent ways of disease prevention and treatment. Indeed, awareness empowers an individual with better choices regarding one’s lifestyle and when to seek medical attention.
In the end, early recognition of signs and symptoms of a heart attack, adherence to preventive measures, and understanding the nature of the pain that a heart attack causes have much to do with heart health and improvement of outcomes. If you have symptoms that may suggest a heart attack, seek emergency medical care immediately for the best outcome of recovery.