Minor Eye Infection: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Symptoms
The symptoms of minor eye infections can be different, based on the type of infection and its severity. The common ones include:
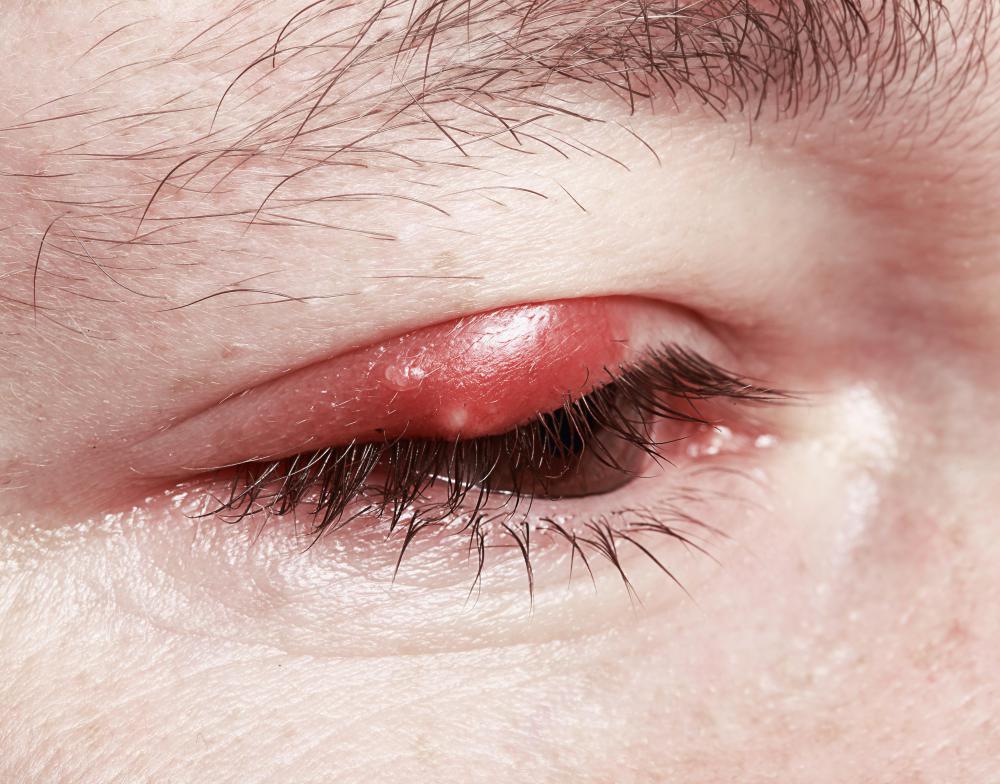
- Redness: The white part of the eye, otherwise known as the sclera, can turn pink or red.
- Itching: An urge to rub or scratch the eyes persistently.
- Discharge: Watery, yellow, or green discharge, particularly in the morning hours.
- Swelling: Puffiness or swelling of eyelids.
- Tearing: Increased production of tears.
- Burning Sensation: Itchy or burning sensation in the eye.
- Blurry Vision: Slightly blurred vision because of discharge or irritation.
- Light Sensitivity: The eyes may show sensitivity to sharp light.
Causes
The minor eye infection is caused by a number of causes, which include:
- Bacterial Infections: Bacteria like Staphylococcus or Streptococcus are responsible for what is commonly referred to as conjunctivitis or pink eye.
- Viral Infections: The virus responsible for the common cold or flu can bring about viral conjunctivitis.
- Allergies: An allergic reaction caused by pollen, dust, or dander of certain animals gives rise to allergic conjunctivitis.
- Foreign Bodies: Dust, dirt, or other minute particles which enter the eye may cause irritation and hence infection.
- Wearing Contact Lenses: Poor hygiene or improper contact lens wear may introduce bacteria or viruses into the eye.
- Chemical Exposure: The eyes are highly susceptible to certain types of chemical exposure or irritants which may lead to a chemical conjunctivitis.
- Fungal Infections: Though rare, fungi also lead to ocular infections, particularly among people whose immunity is lowered.
How to Rectify
The treatment of a minor eye infection involves home remedies and, in some cases, medical treatment from a professional physician: ;
- Warm Compress: Warm compress on the infected eye decreases swelling and gives soothing relief to the patient. Apply this in multiple replications per day.
- Good Hygiene: Wash your hands often and avoid touching or rubbing your eyes. If you wear contact lenses, be keen on good hygiene, including cleaning and replacing them at the time recommended.
- Artificial Tears: Over-the-counter artificial tears can soothe dry irritated eyes and may help flush out foreign particles.
- Avoid Allergens: In cases where an infection is related to allergy, try as much as possible to avoid exposure to such known allergens. Antihistamine eye drops may be used if necessary.
- Antibiotic Eye Drops/Ointments: For bacterial infections, the doctor may prescribe eye drops or ointment containing antibiotics. It is always necessary to complete your prescription, even when symptoms improve.
- Antiviral Medication: In case of a serious infection caused by viruses, your doctor can recommend antiviral medication, though most viral eye infections heal without more than supportive care.
- Rest: Avoid continuous work on computers, bright lights, and tasks that demand concentration.
- Consult a Doctor: In worse conditions, or if the symptoms remain after a couple of days, visit an eye doctor; further medication may be required, or they must assess for grave underlying conditions.
When to Seek Medical Attention
- The pain or discomfort remains
- Increased redness or swelling
- Loss of vision or strong blurriness.
Symptoms not improving after a few days of home treatment.
These steps will easily manage and resolve the minor eye infections; however, it is very important to pay attention to the symptoms and take professional advice where necessary.